When it comes to soundproofing a studio, it is important to address both high and low frequencies to ensure optimal sound quality and reduce unwanted noise. Low frequencies, also known as bass or rumble, can be particularly challenging to control due to their ability to penetrate walls, floors, and ceilings. However, with the right materials and techniques, you can effectively soundproof your studio and create an environment that is ideal for recording, mixing, and mastering.
While many people focus on soundproofing high-frequency noises like speech and music, low-frequency noises are equally important and often more challenging to control. In this article, we’ll discuss how to soundproof low frequencies and what factors to consider when choosing materials and techniques.
Airborne Soundproofing
Airborne sound transmission occurs when sound waves travel through the air from one room to another. To reduce airborne sound transmission, you can use soundproofing materials such as acoustic panels, soundproof curtains, and mass-loaded vinyl (MLV). Acoustic panels and soundproof curtains work by absorbing sound waves, while MLV is a dense material that blocks sound. To achieve optimal results, it is recommended to use a combination of these materials and install them in strategic locations, such as on walls, floors, and ceilings.
Here are some steps you can take to soundproof against airborne sound:
- Install acoustic panels: Acoustic panels are designed to absorb sound and reduce echoes. By installing them on the walls, ceilings, and even the floor of a room, you can effectively reduce the amount of sound that is transmitted through the air.
- Use soundproof curtains or window treatments: Soundproof curtains or window treatments can be an effective way to block out unwanted noise from outside. Look for products that are specifically designed for soundproofing, and be sure to install them properly to ensure maximum effectiveness.
- Use acoustic door seals: Acoustic door seals are designed to reduce the amount of sound that is transmitted through gaps around a door. By installing these seals, you can effectively block out unwanted noise and improve the overall sound quality of a room.
- Install soundproof drywall: Soundproof drywall is a specialized type of drywall that is designed to reduce the amount of sound that is transmitted through walls. This type of drywall is heavier and denser than regular drywall, and it is often used in recording studios, home theaters, and other sound-sensitive environments.
- Consider soundproofing flooring: Soundproofing flooring can help reduce the amount of sound that is transmitted through the floor. Options include carpet with a thick pad, floating floor systems, and specialized soundproofing underlayment.
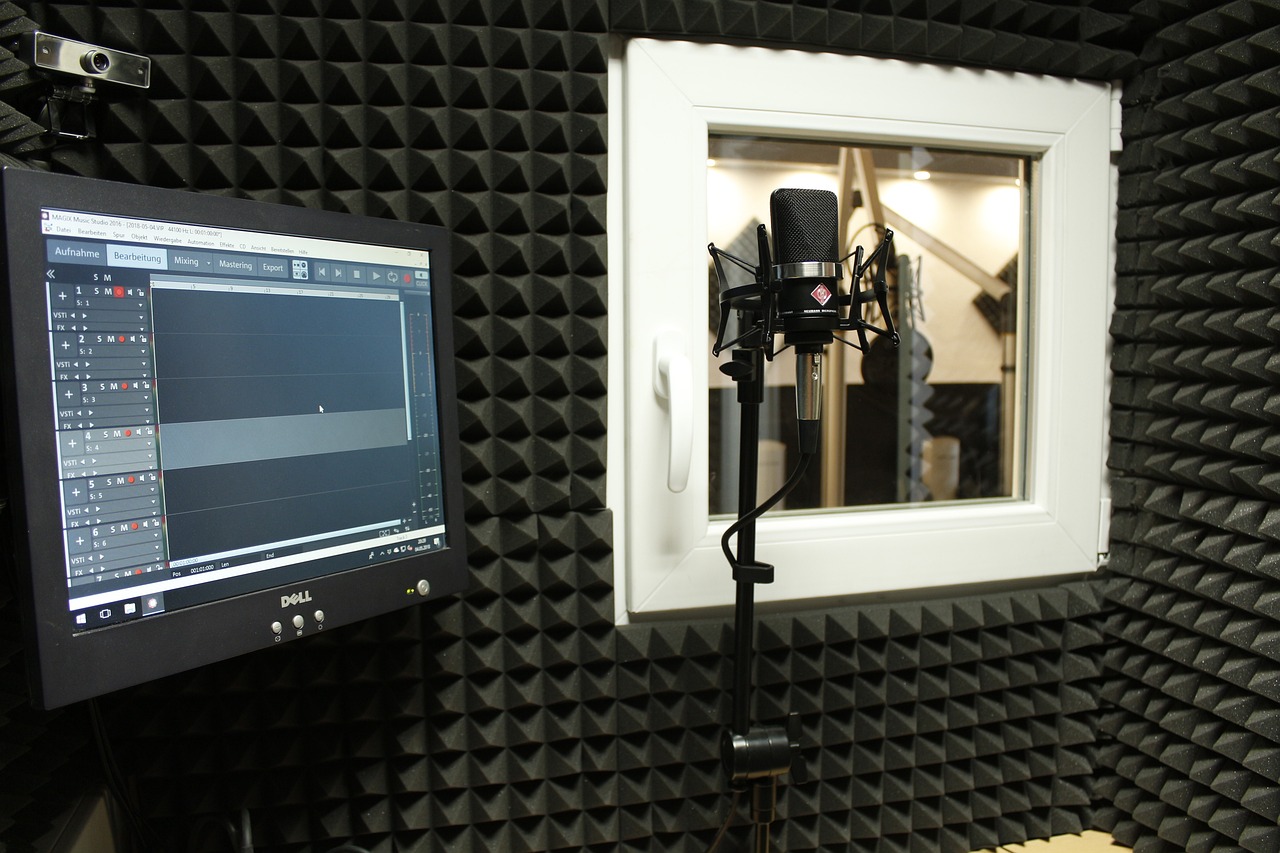

Structural Soundproofing
Structural soundproofing is the process of reducing the transmission of sound through building structures, such as walls, floors, and ceilings. This is an important aspect of soundproofing because it can have a significant impact on the overall sound quality of a room. Structural sound transmission occurs when sound waves travel through the structure, causing it to vibrate and amplify the noise.
To reduce structural sound transmission, you need to address the vibration of the structure itself. This can be done by using materials that are decoupled, such as acoustic flooring systems or resilient channels.
Acoustic flooring systems are specially designed to reduce the transfer of sound between floors by introducing an isolation layer between the subfloor and the finish floor. Resilient channel is a metal channel that is attached to the framing of walls, ceilings, or floors. The channel acts as a barrier, preventing sound from transmitting through the structure.
In addition to decoupling, you can also increase the mass of the structure to reduce structural sound transmission. This can be done by adding soundproofing materials such as mass-loaded vinyl (MLV) or heavy-duty acoustic panels to the walls, floors, and ceilings.
When considering structural soundproofing, it is important to consult with a professional to determine the best approach for your specific needs and budget. In some cases, additional measures may be necessary, such as adding soundproof doors and windows or installing soundproofing materials on the equipment.
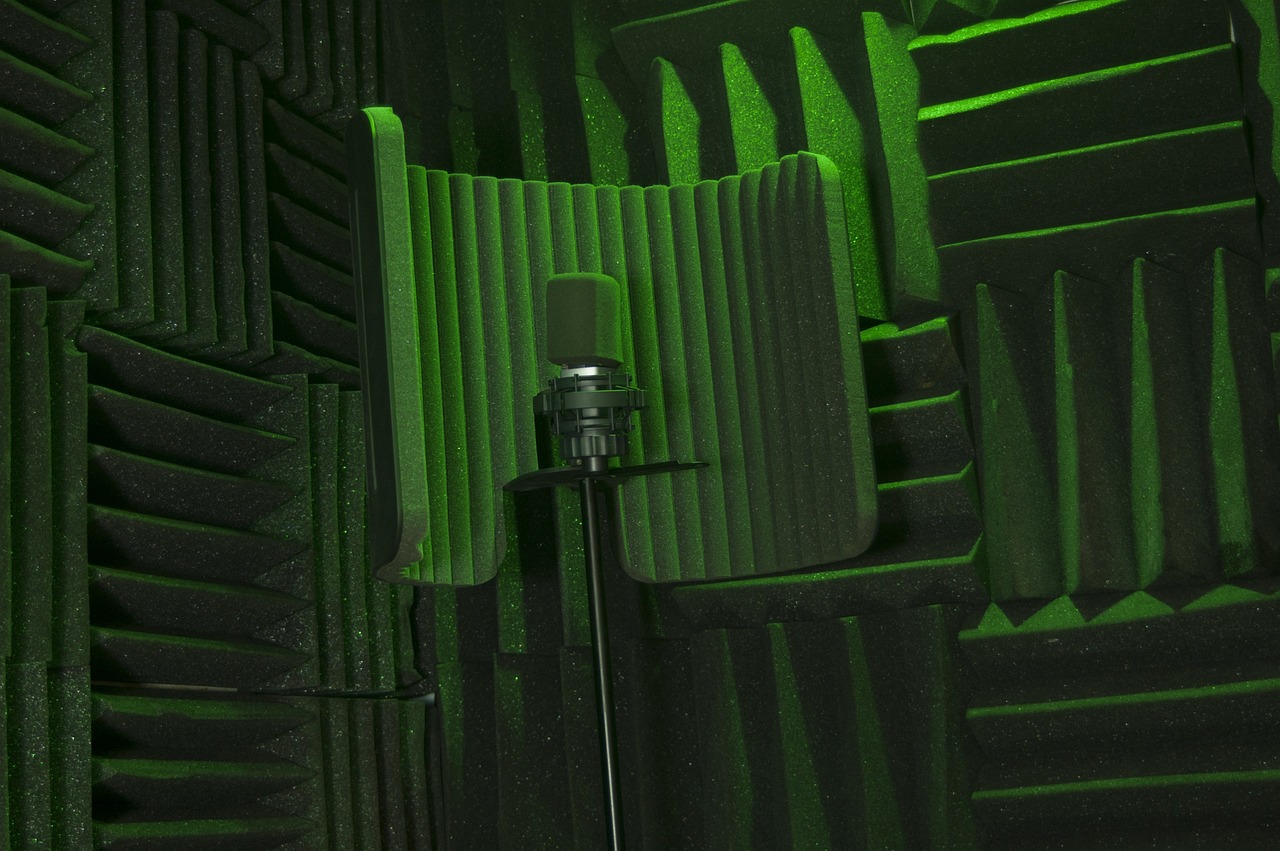

How to soundproof low frequencies in your studio
Here are some steps you can take to soundproof low frequencies in a studio:
- Decouple the walls, floors, and ceilings: One of the most effective ways to reduce low-frequency noise is to decouple the walls, floors, and ceilings from the structure. This can be done by using a layer of acoustic flooring or resilient channel, which acts as a barrier between the structure and the finish surface.
- Add mass to the walls, floors, and ceilings: Adding mass to the walls, floors, and ceilings can help reduce low-frequency noise by absorbing and blocking sound waves. You can do this by using materials such as mass-loaded vinyl (MLV) or heavy-duty acoustic panels.
- Install soundproof doors and windows: Soundproof doors and windows are designed to reduce sound transmission, and they can be particularly effective for controlling low-frequency noise. Look for doors and windows that are rated for high STC (Sound Transmission Class) values, which indicate their effectiveness at blocking sound.
- Use acoustic foam panels: Acoustic foam panels are designed to absorb sound, and they can be particularly effective for reducing low-frequency noise. Install foam panels on the walls, floors, and ceilings, taking care to cover the entire surface area for maximum effectiveness.
- Consider adding soundproofing materials to the studio equipment: Finally, you can also soundproof your studio equipment, such as amplifiers, speakers, and microphones, to reduce low-frequency noise. For example, you can use foam pads or acoustic foam panels to cover the equipment, or you can use shock mounts to decouple the equipment from the surface it is sitting on.
In conclusion, soundproofing low frequencies in a studio requires a multi-layered approach that addresses both airborne and structural sound transmission. By using a combination of decoupling, mass, soundproof doors and windows, acoustic foam panels, and soundproofing materials for your studio equipment, you can effectively reduce low-frequency noise and create an optimal environment for recording and mixing.




 50 Industry Music Production Tips You Must Know
50 Industry Music Production Tips You Must Know




