Distortion is the intentional introduction of harmonic distortion or saturation to audio signals to create a specific sound or effect. Whether it’s overdriving analog equipment, using distortion plugins or hardware processors, or even intentionally clipping the audio signal, distortion can add grit, edge, and aggression to a sound, making it more powerful and intense.
Distortion can also be used to create a vintage or retro sound, or to add warmth, depth and character to a sound. With distortion, you have the power to completely transform a sound or add subtle depth and texture to it.
Distortion can be used in a variety of genres, including electronic to classical music. By experimenting with different types of distortion, you can achieve different effects, from a crunchy and fuzzy guitar sound to a powerful subby bassline, the possibilities are endless.
Distortion in music production can occur in both digital and analog domains. Analog distortion is caused by overloading analog equipment such as guitar amplifiers or tape machines, resulting in a characteristic warm and gritty sound. Digital distortion, on the other hand, occurs when digital audio signals exceed their maximum amplitude, causing a harsh and unpleasant sound.
While analog distortion is often considered more desirable due to its characteristic sound, digital distortion can also be used creatively to achieve unique and modern effects in music production, here’s some examples and how to use it in your music.
Digital:
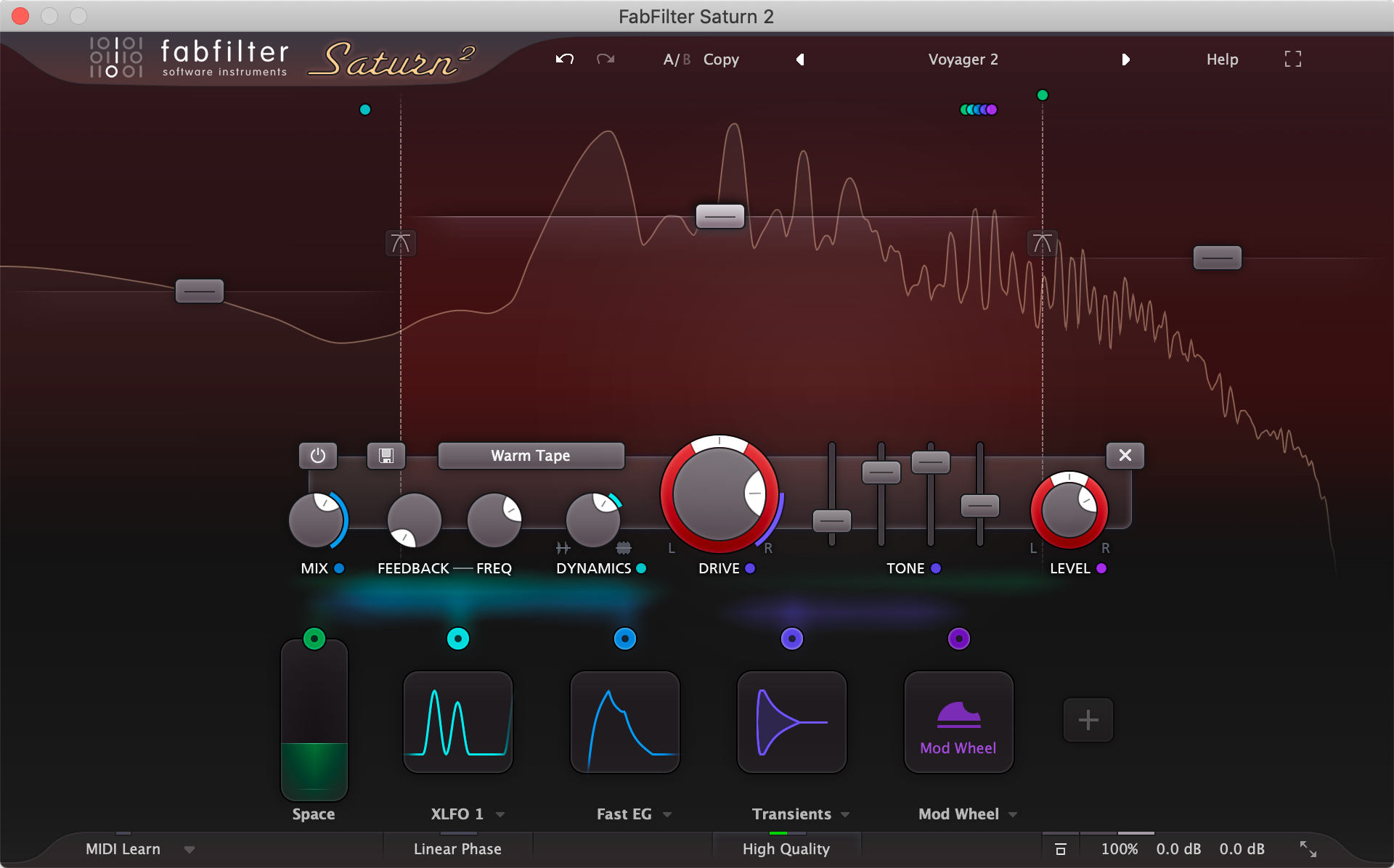
- FabFilter Saturn 2 – A versatile multi-band distortion plugin that offers a wide range of distortion types and saturation modes.
- Use it on individual tracks to add warmth, grit, or distortion to the sound, or on the master bus to give the entire mix a cohesive edge. Try using different distortion types and saturation modes on different frequency bands to create a more complex and interesting sound.
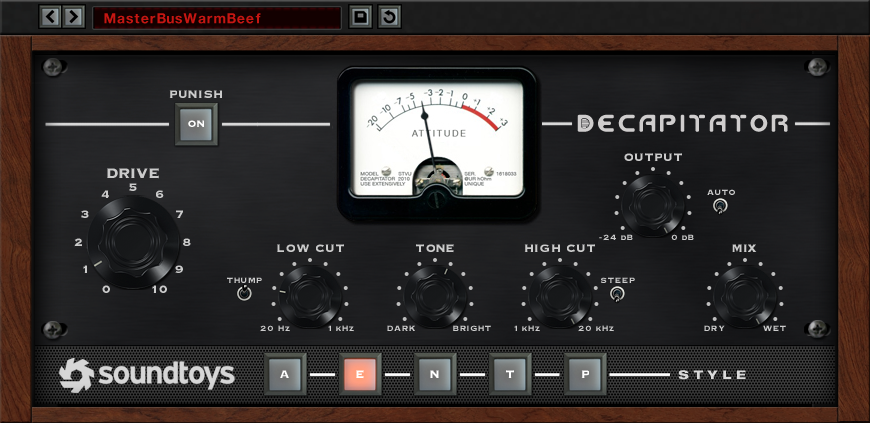
- Soundtoys Decapitator – A plugin that emulates the sound of classic analog saturation and distortion units, with a range of different analog models to choose from.
- Use it to add analog warmth and saturation to individual tracks or the entire mix. Experiment with the different analog models to find the one that best suits the sound you’re going for. Push the Drive and Tone controls to extremes to create more extreme distortion and saturation effects.
- Waves J37 Tape Saturation – A plugin that emulates the sound of tape saturation, providing warmth, richness, and distortion to audio signals.
- Use it on individual tracks or the master bus to add warmth and richness to the sound. Experiment with the different saturation modes to find the one that best suits the sound you’re going for. Use the various controls to adjust the amount and character of the distortion and saturation.

Analog:
- Electro-Harmonix Big Muff Pi – A classic guitar distortion pedal that produces a thick, fuzzy sound.
- Use it on guitar tracks to add a thick, fuzzy distortion effect. Experiment with the various controls to find the right balance of fuzziness and clarity. Use it in combination with other guitar effects, such as delay or reverb, to create more complex guitar sounds.

- Moog Minifooger Drive – An analog overdrive pedal that can produce a range of distortion and saturation effects, from subtle warmth to extreme grit and fuzz.
- Use it on guitar tracks or other instruments to add subtle warmth or extreme distortion effects. Experiment with the various controls to find the right balance of saturation and distortion. Use it in combination with other guitar effects, such as chorus or flanger, to create more complex guitar sounds.

From crunchy guitar riffs to edgy electronic beats, mastering the art of distortion in music production is all about finding the right balance. With a keen ear for sound and a deep understanding of the equipment and techniques involved, producers can carefully select the type and amount of distortion to achieve their desired effect. So crank up the gain and let’s explore the gritty, yet powerful world of distortion in music!




 50 Industry Music Production Tips You Must Know
50 Industry Music Production Tips You Must Know




